Tight Generator Interface support in SoC-E
Introduction
As per the IP-XACT User Guide, IP-XACT defines an API called Tight Generator Interface (TGI) to query, modify, create, and delete IP-XACT XML documents. The standard defines this API in terms of SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) messages in order to make it programming language neutral.
The purpose of the TGI is to abstract from direct XML document manipulation and enable a client/server architecture between IP-XACT design tools and third-party TGI generators.
The TGI uses the concept of handles for objects. Handles are called identifiers (IDs). Objects are entities that can be described in IP-XACT XML documents.
TGI in SoC-E
SoC-E also supports the TGI API for IPs described in IP-XACT XML documents. In SoC-E using these APIs users can access, modify, delete, and create design data according to their own requirements.
Example
TGI API can be used together with SoC-E API and IDS TCL API for querying, creating, or modifying design data available in SoC-E.
An example tcl script for TGI is as below:
soc_read -search_path “input-dir” -file { block1.ipxact.xml , block2.ipxact.xml }
# Get the ID for the component with the given VLNV and add an alternate register in the memory map
set compID1 [ tgi::getID { “Agnisys_Inc.” “Agnisys_Inc.” “block1_model” “1.0” } ]
set compID2 [ tgi::getID { “Agnisys_Inc.” “Agnisys_Inc.” “block2_model” “1.0” } ]
set memMapList [ tgi::getComponentMemoryMapIDs $compID1 ]
set memMapElements [ tgi::getMemoryMapElementIDs $memMapList ]
foreach y $memMapElements {
set regList [ tgi::getAddressBlockRegisterIDs $y ]
foreach z $regList {
set AltReg [ tgi::addRegisterAlternateRegister $z “Altr1” “AltGroup1”]
}
}
}
# Create TOP container using soc_create API
soc_create -type block -name Top_chip -bus ahb -top
# Add apb bus in block using soc_add API
soc_add -type buses -target $compID1 -bus apb
soc_add -type buses -target $compID2 -bus apb
# Add blocks in TOP chip using soc_add API and read blocks using $compID1 and $compID2 TGI
soc_add -type block -target Top_chip -name $compID1 -inst “${compID1}_inst”
soc_add -type block -target Top_chip -name $compID2 -inst “${compID2}_inst”
# Connect blocks in TOP chip using soc_connect API
soc_connect -dest Top_chip -source_inst “${compID1}_inst” -bus apb
soc_connect -dest Top_chip -source_inst “${compID2}_inst” -bus apb
# Using soc_savegraph API we can save graph in tex format
soc_savegraph -name “graph0.nlv” -dir “ids”
# soc_generate API are used to generate output
soc_generate -out {v,sv} -dir ids
#This API is used to show graph
soc_graph Top_chipSchematic View
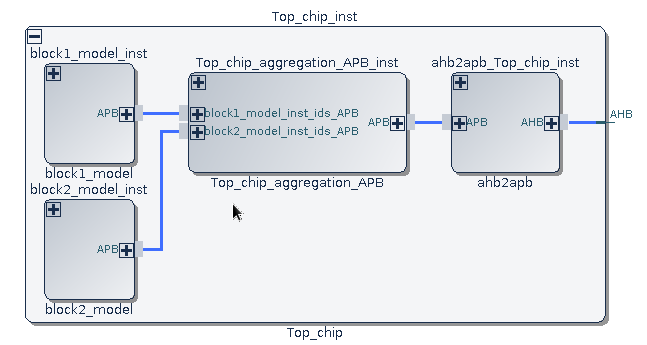
In this example, SoC-E reads an IP-XACT component through the soc_read API. The TGI API obtains the handle of the IP-XACT component, incorporates an APB bus, and instantiates it within a container block named Top_chip. The instance names for the component are block1_model_inst and block2_model_inst. Using the soc_create API, the container block, Top_chip, is established. Subsequently, block1_model_inst and block2_model_inst are connected to Top_chip through an APB bus, as depicted in the graph above.
Conclusion
With the above feature of TGI in SOC-E, users will be able to access and manipulate IP-XACT XML documents according to their requirements. Users can also access, modify, create, and delete documents using TGI rather than generate different IP-XACT XML documents for different requirements.
Pavan Prajapat
Associate R&D Engineer