Avoiding Metastability in Hardware Software Interface (HSI) using CDC Techniques
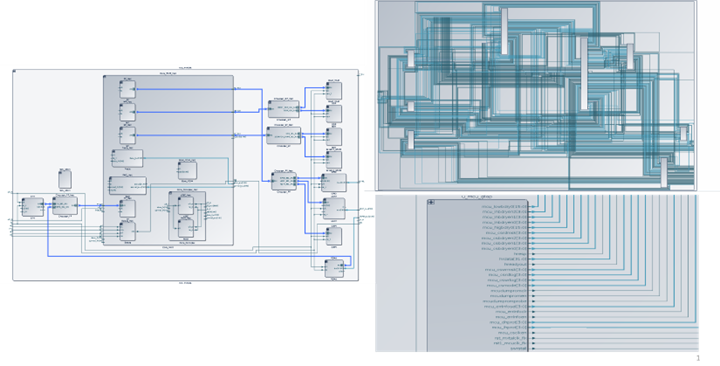
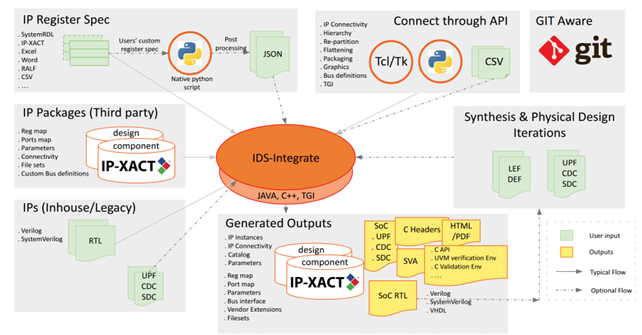
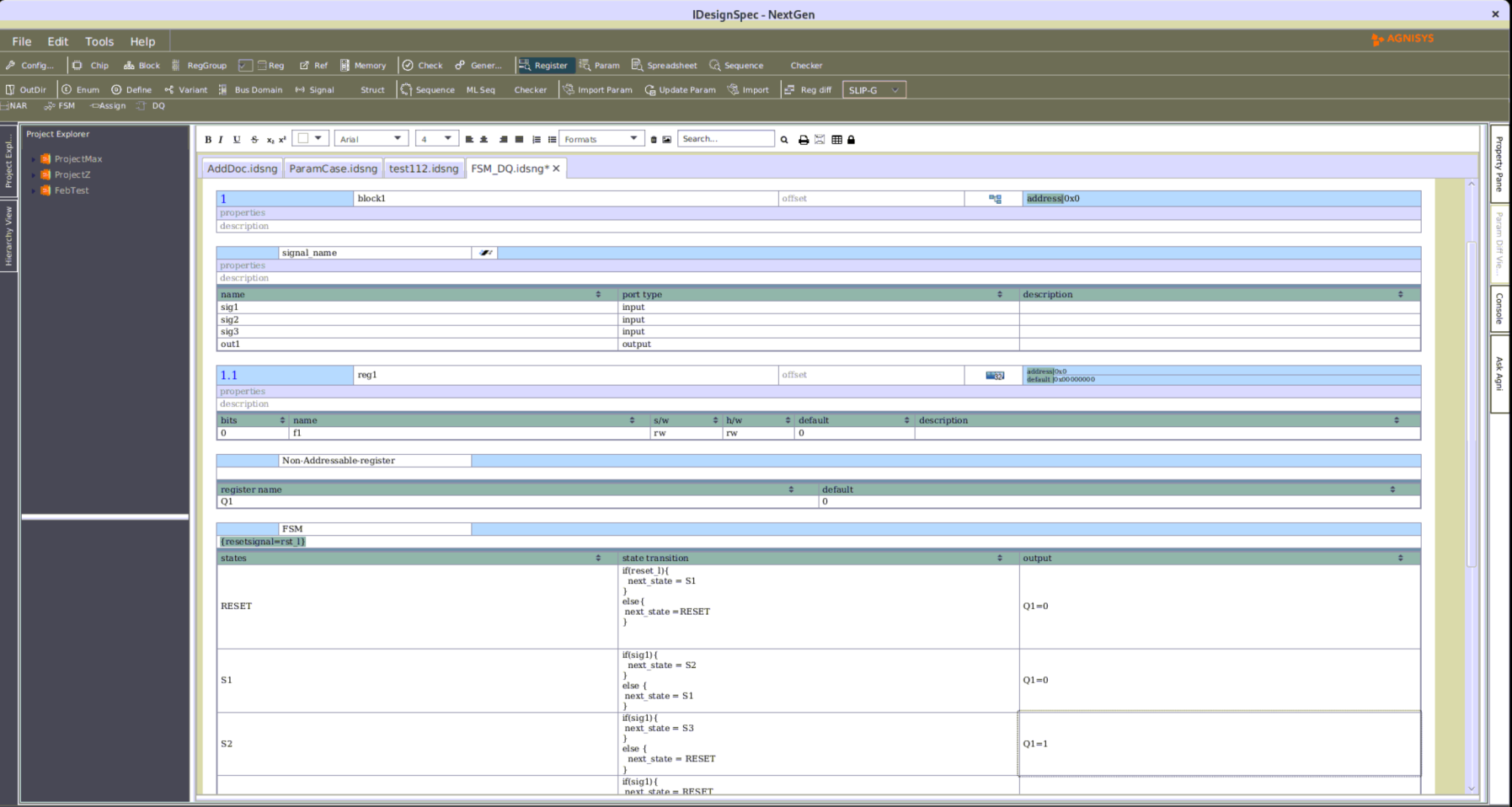
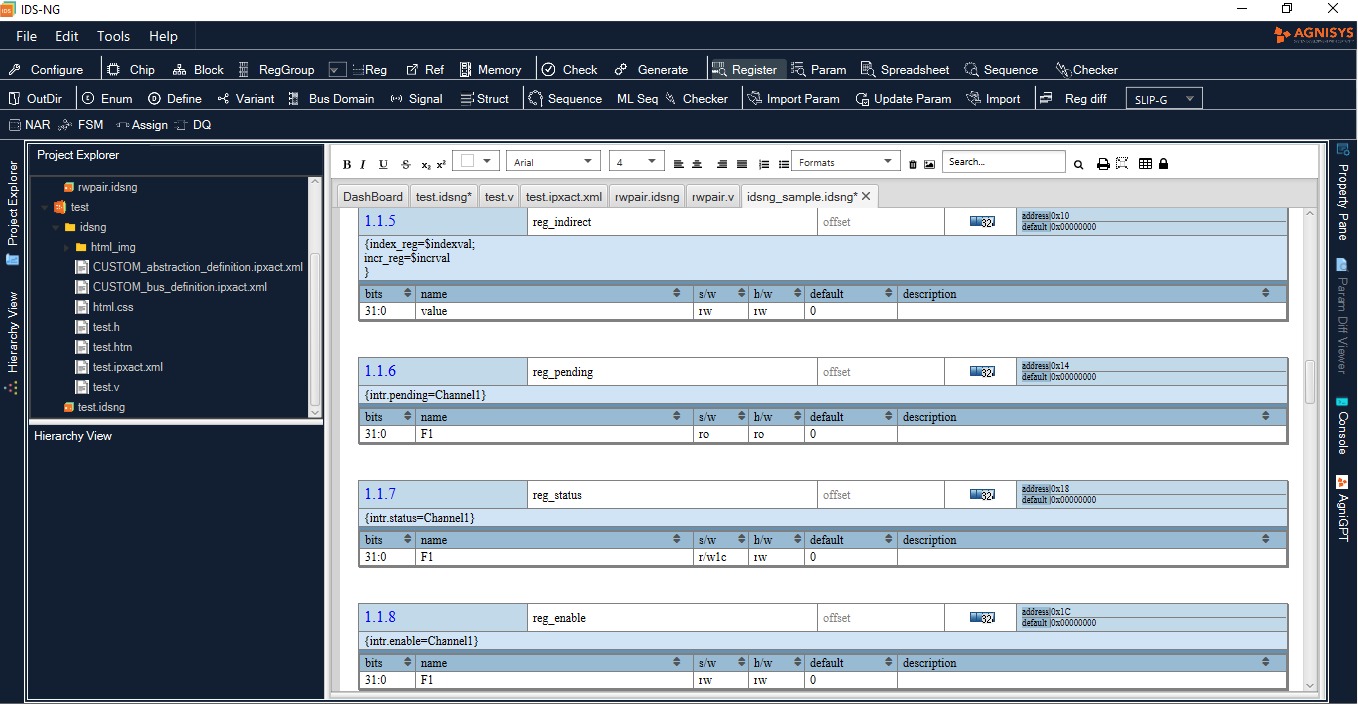
The Agnisys IDesignSpecTM (IDS) Suite supports clock domain crossings (CDCs) from both the software (SW) and hardware (HW) sides. Techniques used to avoid metastability as signals cross from one clock domain to another include:
- Two-Flip-Flop Synchronizer
- Mux Synchronizer
- Handshake Synchronization
– Write
– Read
– Pulse
- Custom Synchronizer
In a CDC design, one clock is either asynchronous to, or has a variable phase relation with respect to, another clock. Speed and power requirements lead to designs with multiple asynchronous clock domains employed at different I/O interfaces and data being transferred from one clock domain to another.
eBook: How Agnisys Eliminates Redundancies in Semiconductor Design, Verification, and Validation
Overcoming the weaknesses of traditional natural language specifications requires writing the specifications in a precise format rather than natural language, and making this format executable so that tools can generate as many files as possible for the design, verification, programming, validation, and documentation teams. Such a solution is available today.
Recent Blog Articles
In today’s semiconductor industry, the most interesting and challenging chips are embedded SoCs. I think it’s worth mentioning that...
In my most recent blog post, I reminisced about childhood toys that let you construct complex structures from simple...
As kids, many engineers enjoyed toys that involved assembling complex designs from simple elements. Whether it was wooden blocks...