Avoiding Metastability in Hardware Software Interface (HSI) using CDC Techniques
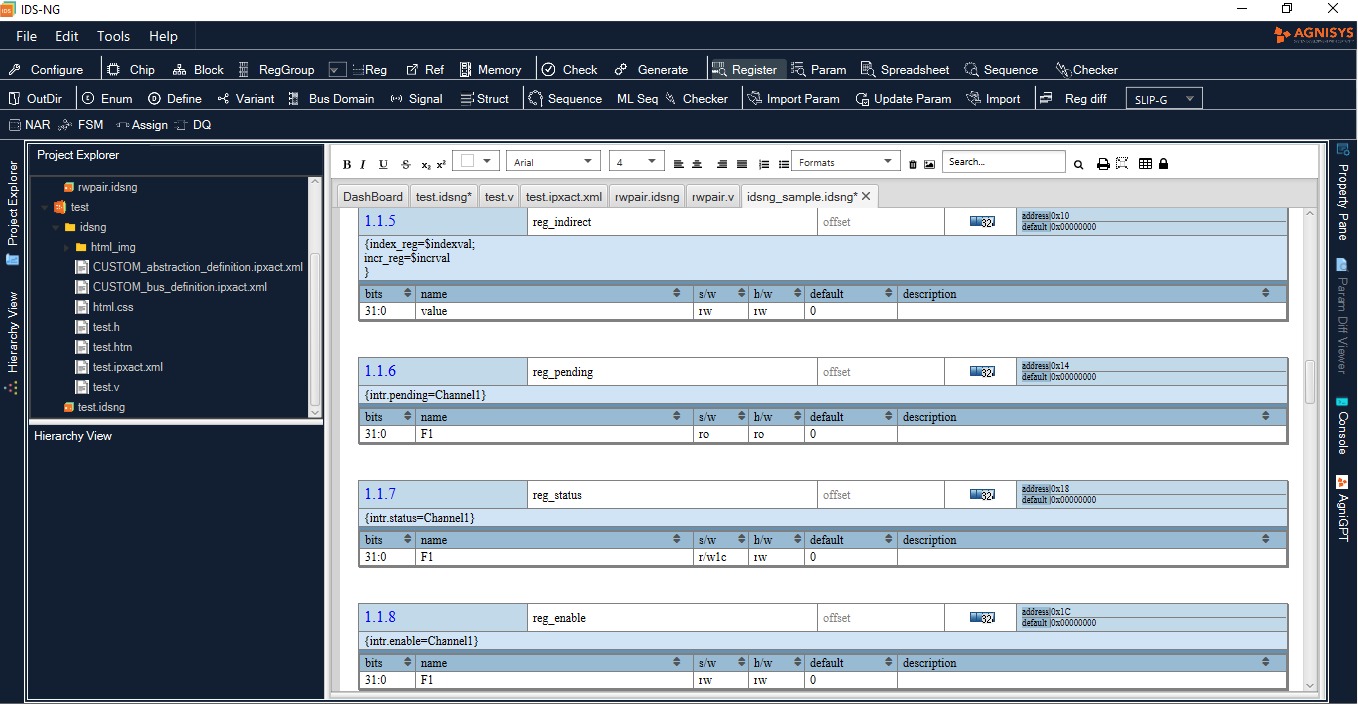
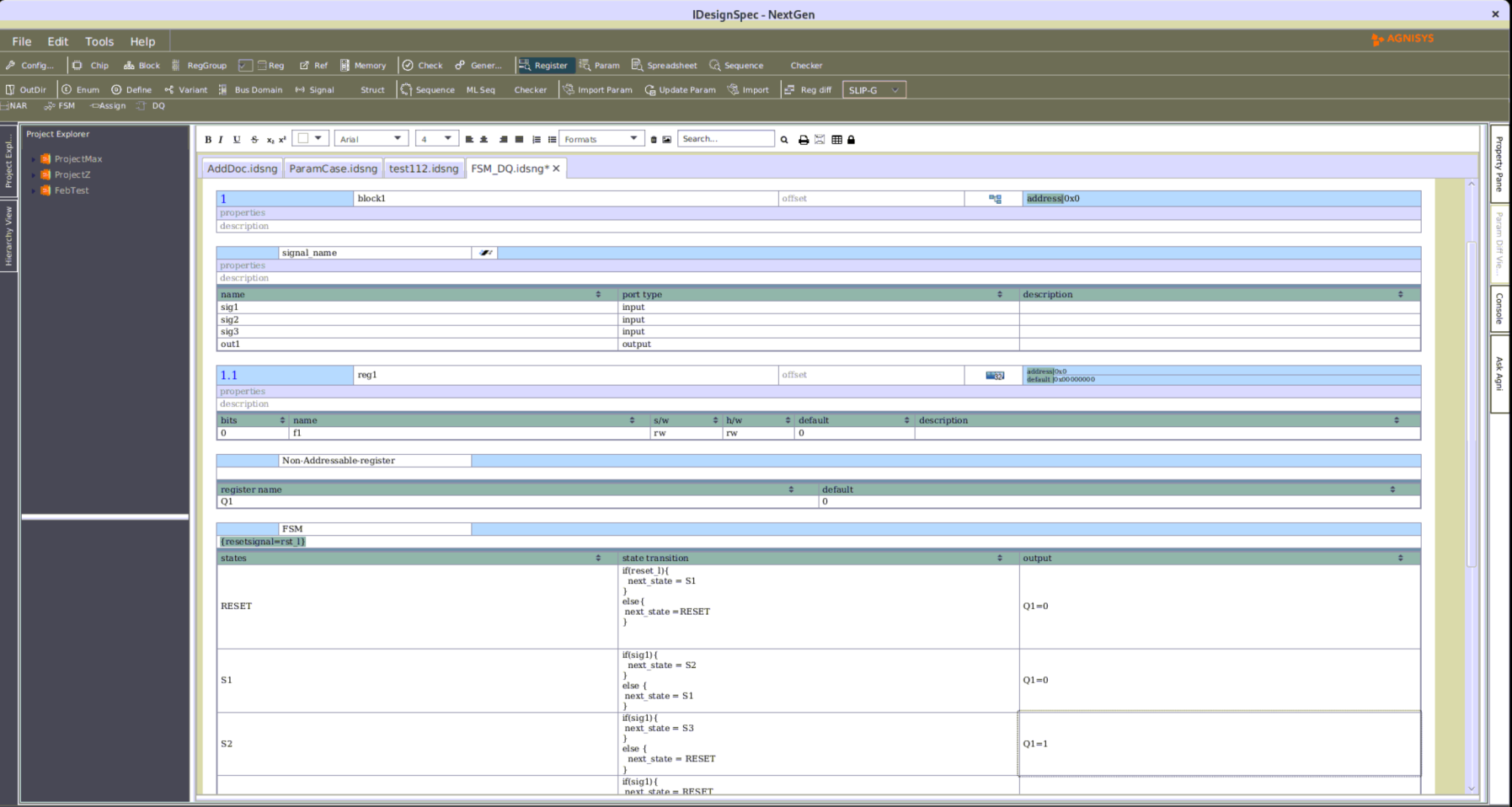
The Agnisys IDesignSpecTM (IDS) Suite supports clock domain crossings (CDCs) from both the software (SW) and hardware (HW) sides. Techniques used to avoid metastability as signals cross from one clock domain to another include:
- Two-Flip-Flop Synchronizer
- Mux Synchronizer
- Handshake Synchronization
– Write
– Read
– Pulse
- Custom Synchronizer
In a CDC design, one clock is either asynchronous to, or has a variable phase relation with respect to, another clock. Speed and power requirements lead to designs with multiple asynchronous clock domains employed at different I/O interfaces and data being transferred from one clock domain to another.
eBook: How Agnisys Eliminates Redundancies in Semiconductor Design, Verification, and Validation
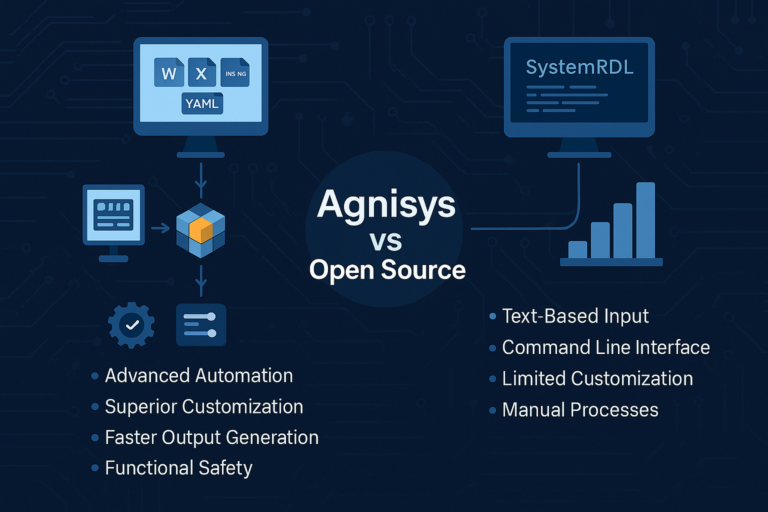
Overcoming the weaknesses of traditional natural language specifications requires writing the specifications in a precise format rather than natural language, and making this format executable so that tools can generate as many files as possible for the design, verification, programming, validation, and documentation teams. Such a solution is available today.
Recent Blog Articles
The Complete One-Stop Solution for Modern SoC Design Challenges In the fast-paced world of semiconductor design, enterprises need robust, flexible...
Agnisys showcases next-generation EDA solutions at DAC 2025, including IDesignSpec Suite v9, IDS-FPGA Launch, AI² and IDS-Integrate Enhancements. BOSTON, MA...
iCatch Technology selects Agnisys’ IDS-Integrate to streamline SoC assembly, ensure design integrity, and accelerate AI chip development. BOSTON, MA, UNITED...