Efficient Global Development: Block Integration & Chip Assembly
There is something anticlimactic and tedious about interconnecting the hundreds or thousands of design blocks that make up a modern system-on-chip (SoC). Architecting the chip is exciting; concocting a novel combination of new blocks, reused blocks, and commercial intellectual property (IP) blocks is a key part of defining a new semiconductor product. There is plenty of room for innovation in the bus or network-on-chip (NOC) structures and in the use of replicated blocks with parallelism to improve performance. Other challenging chip-level architectural topics include clock distribution, power management, design-for-test (DFT) infrastructure, and layout-aware partitioning.
Designing the new blocks is also challenging, and one of the biggest efforts on any SoC project. Today’s blocks are yesterday’s chips, so the scope and complexity of each block demands a high degree of expertise. There are many opportunities for innovation at the block level; in addition to the fresh designs, the reused and commercial IP blocks are often customized for use in the new chip. Designers cherish their jobs for early collaboration with chip architects and detailed block design, fostering enthusiasm and dedication in their work.
Top-Level Hookup is Tedious, Time-Consuming, Subject to Errors and Spec Changes
The third phase of design—hooking all those blocks together into the top-level chip—is a rote task in comparison. This might seem like a simple step, and it’s not rocket science, but it is a significant effort. Consider, for example, an SoC with 400 block instances, with an average of 100 ports each. That means that 40,000 connections must be made to interconnect them. It would be a long and tedious task for a designer to type 40,000 connections in a text editor to create the top-level register-transfer-level (RTL) description.
I’m sure that you’re now crying “But buses!” and, of course, wherever a group of ports forms a multi-bit bus specifying the connections is much easier. On the other hand, large chips are hierarchical so there are multiple levels of assembly required to end up with your complete chip. A single signal running from a leaf-level block up to the top level and then back down to another leaf block might go through a dozen or more connections and renames. Just keeping track of all this is a non-trivial part of the effort.
Similar but different signals and bus names exacerbate the problem. Multiple instantiations of a block generally connect to signal names that differ only in prefixes or suffixes. Again, it’s hard to keep all of this in mind when typing in connections by hand. Mistakes are bound to happen, due to confusion over similar names as well as accidental typos. Every mistake is a design bug that must be triggered and detected in simulation, fixed, and then re-simulated to confirm correctness.
There is yet another wrinkle: the top-level chip architecture and specification changes many times throughout your project. You may find when writing the RTL code, synthesizing it, or placing and routing the resulting netlist that some of the architectural assumptions must change. Your product marketing team might add new features to the specification, perhaps in response to a new market opportunity or the introduction of a competitive chip. Every time that your chip specification changes, there are ripple effects on the design. Often, this includes the top-level interconnect, in which case your designers have to manually make the necessary changes adding not only to the project timeline but potentially introducing potential errors in the process.
Navigating the intricacies of top-level chip hookup is undoubtedly a complex endeavor, marked by tedious manual connections and susceptibility to errors, especially in large-scale SoCs. Enter Agnisys’ PSS Compiler, a game-changer in simplifying this arduous phase. By leveraging the Portable Stimulus Standard (PSS), it streamlines the specification and verification process, significantly reducing the risk of errors and expediting design timelines. Additionally, Agnisys offers seamless integration with UVM testbench methodologies and UVM Register Model Examples, ensuring a cohesive and error-resistant top-level design experience. Embrace efficiency and precision in your chip design journey with Agnisys’ innovative solutions.
Automation for Block Integration and Chip Assembly
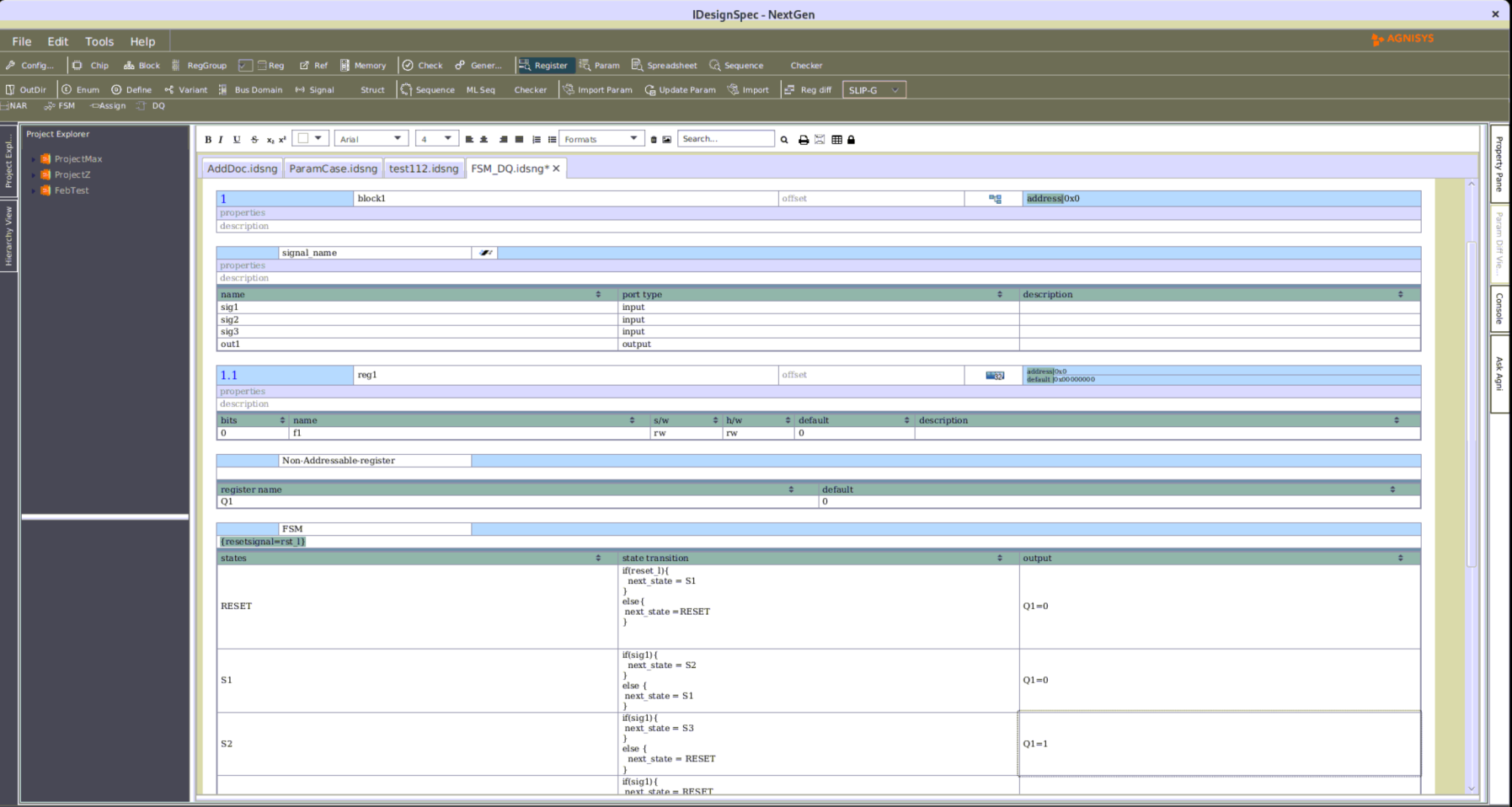
At Agnisys®, we heard from our customers that the process of block integration and chip assembly was a problem, and we decided to see if there was a way to use our expertise in specification automation to provide a solution. The result is IDS-Integrate™, one of the components of our IDesignSpec™ (IDS) Suite of products. IDS-Integrate™ is a flexible and customizable environment for design assembly that supports both your own designs and commercial IP blocks. It fully supports the IP-XACT (IEEE 1685-2014) standard used by many IP providers to document their offerings.
IDS-Integrate™ uses a simple but powerful specification format for you to describe the interconnection of your blocks. Wildcards make it easy to deal with similarly named ports and signals. You can run in command mode using our IDS-Batch™ solution or use our intuitive graphical interface in IDesignSpec™ GDI. Other capabilities include:
- Generating major subsystems with the flexibility to customize or configure
- Automatically adding instances to the design, making connections, restructuring, etc.
- Viewing the resulting schematics for design analysis
- Running design rule checks to endure IP and SoC quality
- Supporting hierarchical specification of block interconnections

I’ll bet that by now you’re crying “But buses!” again. The top level of your SoC probably contains multiple types of buses, and often they can’t be simply connected by wires. A system may require a bus aggregator to combine multiple buses of the same type. When transferring from one bus to another of a different type, the system needs a bus bridge. Additionally, a multiplexer may be necessary to select from among multiple bus sources. We have a solution for this dilemma as well. For standard buses such as AHB and APB, IDS-Integrate™ automatically generates RTL aggregators, bridges, and multiplexors as needed to satisfy your interconnection specification.
For example, the AHB interfaces on two IP blocks can be aggregated into a single bus to connect to external chip pins. Similarly, if the design includes an IP block using AHB and IP blocks with APB interfaces, IDS-Integrate™ can automatically generate an AHB-to-APB bus bridge between the high-speed system bus and the lower-speed peripheral bus. Our Smart Assembler technology automatically integrates and connects all our generated blocks with your blocks.
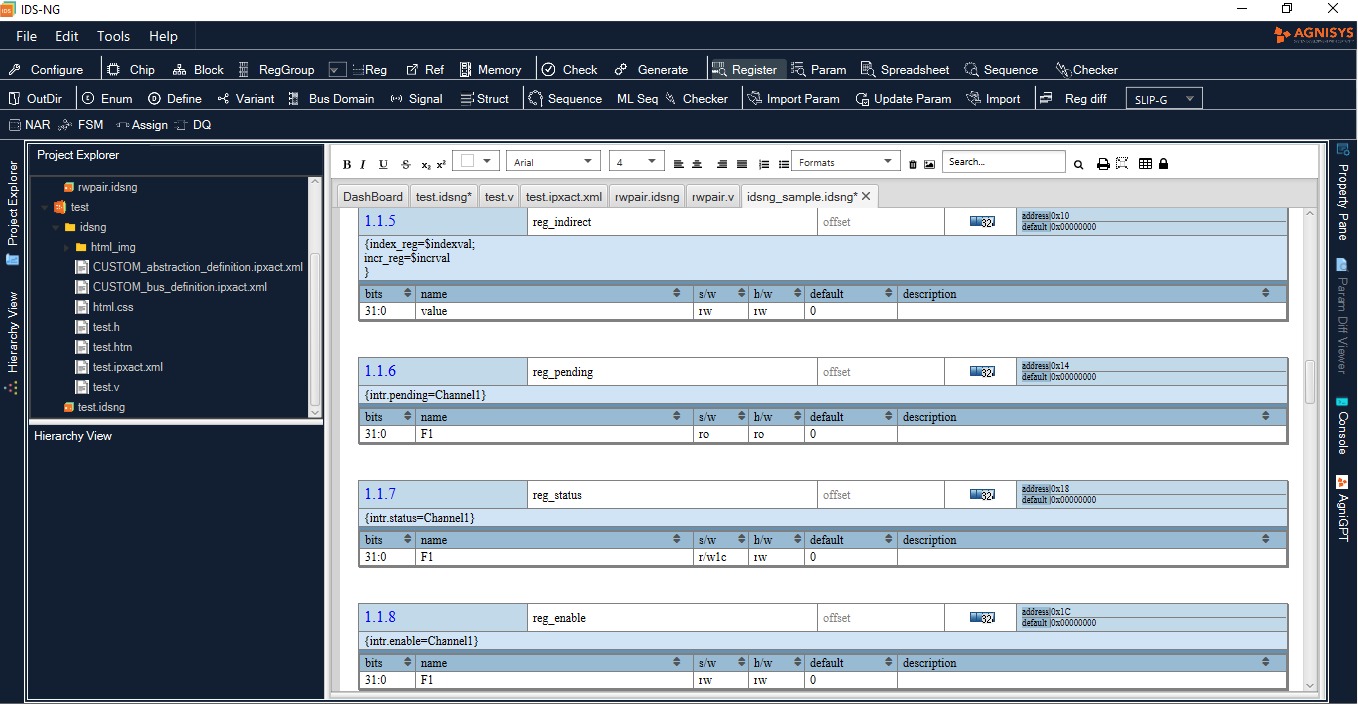
As you would expect, IDS-Integrate™ handles all types of RTL blocks generated by the other tools in the IDesignSpec™ Suite. Both IDesignSpec™ GDI and IDS-Batch™ generate the RTL designs for registers, register groups, and memories based on your specifications. Beyond registers, IDS-IPGen™ is a library of RTL generators for standard IP functions such as AES, DMA, GPIO, I2C, I2S, PIC, PWM, SPI, Timer, and UART. You can easily configure and customize these blocks to meet your chip-specific requirements. IDS-Integrate™ automatically connects all these blocks in the SoC using its Smart Assembler technology.
IDS-Integrate™ is not limited to the blocks we generate ourselves. Smart Assembler can also automatically connect your custom design blocks. You can select a set of ports on a block and direct IDS-Integrate™ to automatically create the template for a new block with the same set of (mirrored) ports and then connect the two blocks. Smart Assembler can also connect existing blocks with mirrored ports and can even connect arbitrary blocks if you specify the connections required. Efficiently populate your SoC with interconnected IP even before fully specifying RTL functionality, thanks to these capabilities. You can even have IDS-Integrate™ “promote” selected ports to the top level so that they can become external chip pins.
IDS-Integrate™ is an enterprise-level solution, so it can support your design teams spread around the world and integrate all their IP blocks into the full SoC. It provides a complete solution for the assembly and interconnection of design blocks, providing increased designer efficiency and a shorter time to market. Your designers can concentrate on differentiating features rather than tedious manual connections. Best of all, every time that your specification changes you can simply rerun IDS-Integrate™ at the push of a button. Your RTL design and specification remain synchronized with no manual effort.
Specification Automation for Seamless Integration
Agnisys® addresses the challenges of block integration and chip assembly head-on with IDS-Integrate™, a testament to the company’s commitment to innovation. This component of the IDesignSpec™ Suite leverages Agnisys’ expertise in specification automation, providing a flexible and customizable environment for design assembly. IDS-Integrate™ supports your proprietary designs and commercial IP blocks, adhering to the IP-XACT (IEEE 1685-2014) standard. Whether you opt for command mode using IDS-Batch™ or the intuitive graphical interface in IDesignSpec™ GDI, IDS-Integrate™ streamlines major subsystem generation, automatic instance addition, interconnection, and design analysis, ensuring efficiency throughout the design process.
Enterprise-Level Solution for Global Design Teams
Agnisys® goes beyond conventional solutions with IDS-Integrate™, offering an enterprise-level paradigm for global design teams. This tool seamlessly integrates all IP into the full SoC, providing a comprehensive solution for assembly and interconnection of design blocks. The challenge of diverse buses is met with IDS-Integrate™ automatically generating RTL aggregators, bridges, and multiplexors as required by the interconnection specification. It caters to standard buses like AHB and APB, ensuring a hassle-free design process. IDS-Integrate™, equipped with Smart Assembler technology, not only handles Agnisys-generated blocks but also seamlessly connects custom design blocks, supporting an efficient and synchronized design cycle. Embrace a shorter time to market and increased designer efficiency with Agnisys’ IDS-Integrate™, a revolutionary solution in specification automation.
Your SoC development process is faster, better, and less expensive with the advanced specification automation solutions from Agnisys. For further details or to request an evaluation, please send an email to marcom@agnisys.com.
Before you begin your next chip development project, consider Agnisys for Heterogeneous Systems Correct-By-Construction.
Anupam Bakshi
There are multiple causes for design errors, but some of the most common are related to the design specifications and how they are distributed and maintained throughout the product development lifecycle. Learn how to address this issue by reading The IC Designer’s Guide to Automated Specification of Design and Verification, for Better Products.